Short ineresing facts about Madagascar
- Republic of Madagascar is the fourth largest island in the world, approximately (587,000 2 km). The only larger islands are Borneo, Greenland and New Guinea.
- Almost all of the plant and animal species found on the Madagascar Island are unique to this island.
- Madagascar has two seasons, a dry cooler season which starts in May and last until October and a hot rainy season which starts in November and last until April.
- The capital of this island is Antananarivo. This city is also the Madagascar’s most populated city.
- The population of Madagascar : 21,290,000.
- Madagascar is one of the poorest countries in Africa. The people in this territory face many problems including poor health care, a poor educational system, economic problems and malnutrition.
- Most of the population or better to say 52% maintain their indigenous religious beliefs, other 41% are Christian and 7% are Islam.
- Madagascar has two official languages, first is French and second Malagasy.
- Madagascar Island was under French rule from 1895-1957.
- This island has lost more than 80% of its original forest land since humans arrived on this place about two thousand years ago.
About Madagascar
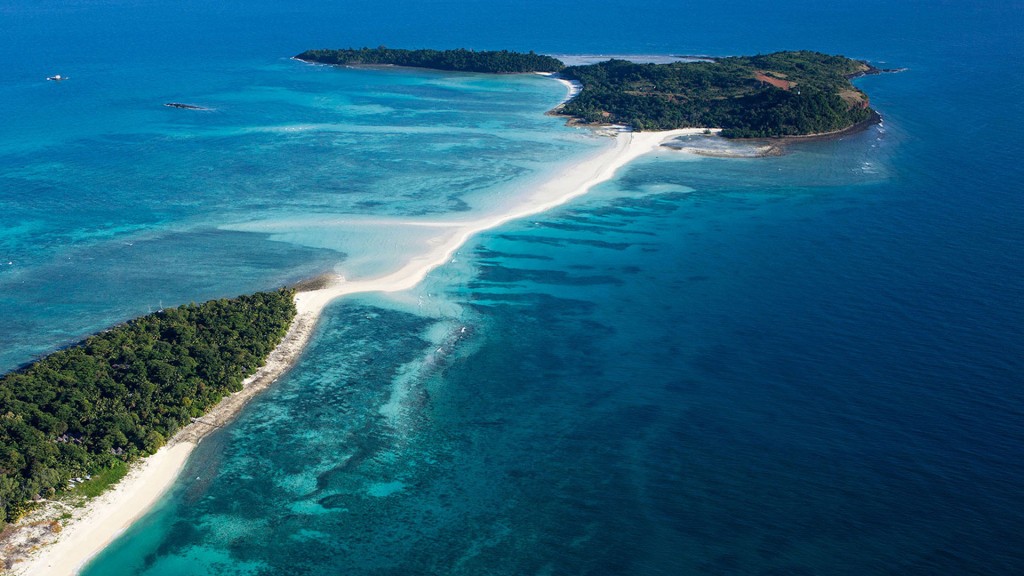

Madagascar is officially known as the Republic of Madagascar. This country is an island country in the Indian Ocean and is located in the coast of Southeast Africa. The nation comprises the island of Madagascar which is the fourth-largest island in the world, as well as numerous smaller islands near this place. A long time ago Madagascar was part of India but this place split from India around 85 million years ago, allowing plants to evolve and native animals in relative isolation. Madagascar is a very biodiversity hotspot . Over 90 % of its wildlife is found nowhere else in different places in the world.
The Republic of Madagascar was ruled by a fragmented assortment of shifting sociopolitical alliances until the late 18th century. Beginning in the early 20th century, most of the island was ruled and united as the Kingdom of Madagascar.
In 2012, the population of Madagascar was approximately 22 million people, 90% of them live on less than 2 $ per day. French and Malagasy are both official languages of the Republic of Madagascar. The majority of the population adheres to Christianity, traditional beliefs or an amalgamation of both. Agriculture and ecotourism, paired with greater investments in health, education and private enterprise, are key elements of development strategy in Republic of Madagascar.
Etymology

The island of Madagascar is called Madagasikara in the Malagasy language. The island’s appellation “Madagascar” is not of local origin but rather was popularized by Europeans in the middle Ages . Years later Portuguese explorer Diogo Dias landed on this island and christened it Sao Loureno, but this name was preferred and popularized on Renaissance maps. The name Madagascar was first recorded in the memoirs of 15th century by explorer Marco Polo as a corrupted transliteration of the Mogadishu name. This name which we use today appears to have been used by the Malagaesy local population to refer to this place.
Geography
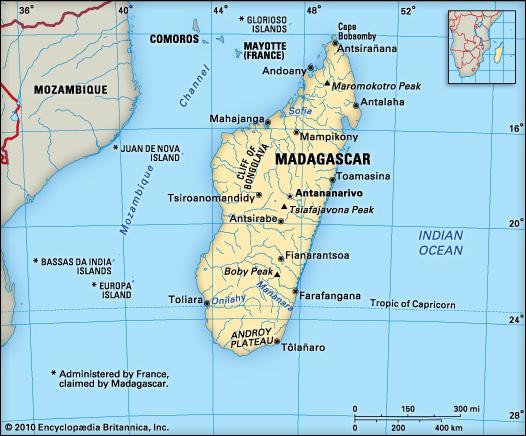
With its 593,000 2 km territory, this island is the fourth-largest island and the world’s 47th largest country. Madagascar lies mostly between longitudes 43°E and 51°E and latitudes 12°S and 26°S. Neighboring islands near Madagascar includes the French territory of Réunion and the country of Mauritius to the east, the French territory of Mayotte to the north west and the state of Comoros .
Climate
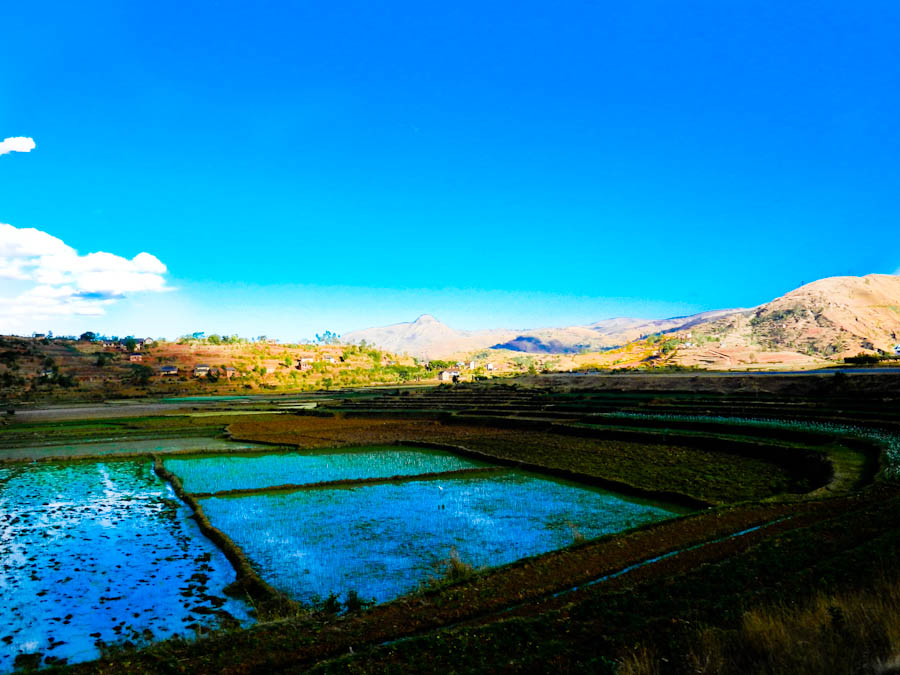

The combination of northwestern monsoons and southeastern trade winds produces a hot rainy season (from November to April) with frequently cyclones, and a relatively cooler very dry season (from May to October). Rain clouds originating over the Indian Ocean discharge much of their moisture over the Madagascar’s eastern coast. 10 years ago Cyclone Gafilo became the strongest cyclone ever recorded to hit the Republic of Madagascar. The storm killed more than 172 people and left more than 215,000 homeless and caused over than $ 250 million in damage.
Ecology
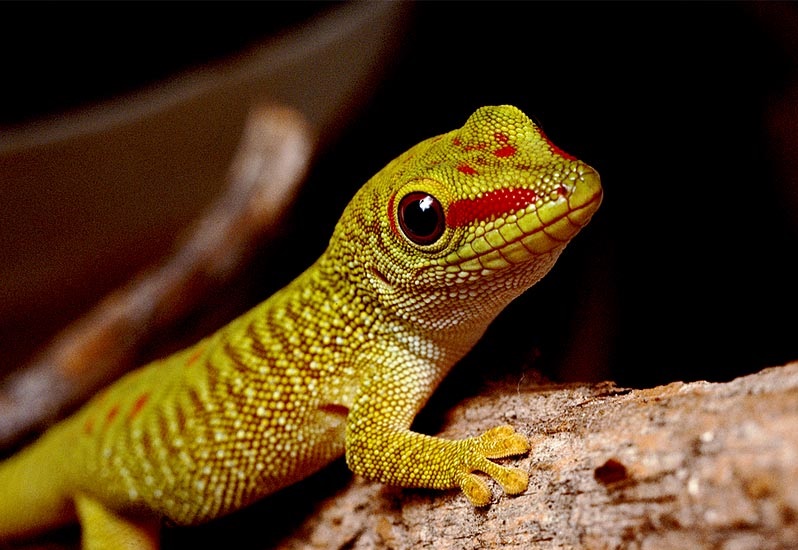

Republic of Madagascar is home to an abundance of animals and plants found nowhere else on Earth. Approximately 90% of all animal and plant species found in Madagascar are endemic, including here the lemurs which is a type of prosimian primate, many birds and the carnivorous fossa . This ecology diversity has led some ecologists to refer to Madagascar as the “eighth continent”. In 2010 this island has been classified by Conservation International as a biodiversity hotspot. More than 85 % of Madagascar’s more than 13,900 plant species are found nowhere else in the world, including 5 plant families. The Madagascar Island is home to around 170 palm species. A lot of those native plant species are used as herbal remedies for a variety of afflictions and different specialties.
The drugs vincristine and vinblastine , used to treat leukemia, Hodgkin’s disease and other cancers. The traveler’s palm, which is known in this place as endemic and ravinala to the eastern rain forests, is highly iconic of Republic of Madagascar and is featured in the national emblem as well as the Airport Madagascar logo. Like its flora, Madagascar’s fauna is exhibits and diverse a high rate of endemism. By 2012, there were formally 105 species and subspecies connected with lemur, some of them were described in the past by zoologists. They are almost all classified as vulnerable, endangered or rare. At least 15 species of lemur are getting to be extinct since man arrived in this island, all which were larger than the particular surviving lemur species.Over 350 species of birds have been recorded in this island, of which over 60% (including 4 families and 44 genera) are endemic.A number of other mammals, including here the kind of cat-like fossa, which is endemic to Madagascar. The few genera and families of reptile that have reached Madagascar have diversified into over 300 species, more than 93 % of these being endemic. This island is home to two-thirds of the world’s chameleon species, including the smallest known in the earth.
Another interesting facts about Madagascar is that endemic fish of Madagascar include 150 species, 16 genera and 2 families, primarily inhabiting the island’s fresh water rivers and lakes. More than 670 species of terrestrial snail are endemic, as are a majority of the island’s scarab beetles, butterflies, spiders, lacewings and dragonflies. Environmental challenges Madagascar’s varied flora and fauna are endangered by human activity. Since the arrival of humans around 2,400 years ago, Madagascar has lost more than 90 % of its original forest.. According to a conservative estimate, about 40 % of the island’s original forest cover was lost from the 1950s-2000, with a thinning of remaining forest areas by 85%.
Government – Structure

Antananarivo is the economic and political capital of Madagascar.
Madagascar is a semi-presidential representative democratic republic where president is the head of state and selects a prime minister which recommends candidates to the president to form his cabinet of ministersThe constitution establishes independent legislative, executive and judicial mandates and branches a popularly elected president limited to three five-year terms. The last presidential election was held on 3 December 2006. This process resulted in the re-election of Marc Ravalomanana, but then from whom executive power was unconstitutionally transferred to Andry Rajoelina three years later in March 2009.
Economy
During Madagascar’s First Republic, France has a lot influence Madagascar’s economic policy and planning and served as its key trading partner. Government initiatives such as a rural development program and state farms were established to boost production of commodities such as coffee, cattle, rice, palm oil and silk.Madagascar’s G.D.P in 2009 was estimated at $ 9 billion, with a per capita G.D.P of $450. Approximately 69 % of the population lives below the national poverty line threshold of 1$ per day. The agriculture sector constituted 295% of Malagasy G.D.P in 2011, while manufacturing formed 15 % of G.D.P.
Tourism focuses on the niche eco-tourism market, capitalizing on island’s unique biodiversity, unspoiled, lemur species, national parks and natural habitats. An estimated 365,090 tourists visited Madagascar in 2008, but the sector has declined two years later because of the political crisis with 185,000 tourists visiting in 2010 and 175,800 in 2011. Natural resources and trade Madagascar’s natural resources include a variety of unprocessed mineral resources and agricultural. Key mineral resources include various types of semi-precious and precious stones, and this island currently provides half of the world’s supply of sapphires. Other key agricultural resources include shrimp, coffee and lychees . This product were discovered near Ilakaka in the late 1995s. Madagascar also holds one of the world’s largest reserves of ilmenite as well as important reserves of coal, chromite, cobalt, iron, copper and nickel. Madagascar is the world’s principal supplier of cloves, ylang-ylang and vanilla. Several major projects are underway in the mining, gas and oil sectors that are anticipated to give a significant boost to the economy.
Exports formed 28 % of G.D.P in 2009. Most of the country’s export revenue comes from the textiles industry, shellfish and fish, cloves, vanilla and other foodstuffs. Country of France is Madagascar’s main trading partner, although the Japan, Germany and United States also have strong economic ties to the republic of Madagascar. The Madagascar- Business Council was formed in May 2003, as a collaboration between Malagasy artisan producers and USAID to support the export of local handicrafts to foreign markets. Imports different things such as fuel, foodstuffs, consumer goods vehicles, electronics consume and capital goods an estimated 52 % of GDP. The main sources of Madagascar’s imports include China, France, Mauritius Hong Kong and Iran.
read also about Madagascar passport visa free countries
Infrastructure and media

In 2010, Madagascar had approximately 8,000 kilometers of paved roads, 860 kilometers of railways and 435 km of navigable waterways. Largely paved national routes connect the six largest regional towns to Antananarivo, with unpaved routes and minor paved providing access to other population centers in each district. Antananarivo is connected to Ambatondrazaka, Toamasina and Antsirabe by rail, connects Manakara to Fianarantsoa. One of the most important seaport in Madagascar is located on the east coast at Toamaesina.Running electricity and water are supplied at the national level by a government service provider, Jirama which is unable to service the entire population. As of 2010, only 6.5% of Madagascar’s fokontany had access to water provided by Jirama, while other 9.8 % had access to its electricity services.
More than 56% of Madagascar’s power is provided by hydroelectric power plants with the remaining 45% provided by different diesel engine generators. Internet access and mobile telephone are widespread in urban areas but remain limited in rural parts of the Madagascar. Approximately 30% of the districts are able to access the nations’ several private telecommunications networks via land lines or mobile telephones. Access to the internet has grown dramatically over the past decade, with an estimated 361,000 residents of Madagascar accessing the internet from home or in one of the nation’s many internet cafes in December 2012.
Health

In 2011 Republic of Madagascar had an average of 3 hospital beds per more than 10,000 people and a total of 3,200 doctors, 5,700 nurses, 390 community health workers, 180 pharmacists and 60 dentists for a population of 22 million people. 14.6 % of government spending in 2009 was directed toward the health sector. The fertility rate in 2009 was 4.5 children/woman, declining from 6.5 in 1991. Teen pregnancy rates of 14.5 % in 2011. In 2011 the maternal mortality rate was 444 per 100,100 births, compared to 383 in 2008 and 485, 5 in 1991, indicating a decline in perinatal care following the 2009 coup.The infant mortality rate in 2012 was 42 per 1,000 births, with an under-five mortality rate at 65 per 1,000 births. Malaria, Schistosomiasis, and sexually transmitted diseases are common in the Republic of Madagascar, although infection rates of AIDS remain low relative to many countries in mainland Africa, at only 1% of the adult population.
The malaria mortality rate is also among the lowest in Africa and in other places, at 8.8 deaths per 120,000 people, in part due to the highest frequency use of insecticide treated nets in Africa. Adult life expectancy in 20010 was 65 years for men and 68 years for women.
Education

The first formal school was established in 1819 at Toamasina by members of the London Missionary Society, this school was made in European style. The LMS was invited by King Radama I to expand its schools throughout Imenrina to teach numeracy to aristocratic and basic literacy children. The schools were closed by Ranavalona I in 1836 but they were reopened and expanded in the decades after her death. By the end of the 19th republic of Madagascar had the most developed and modern school system in precolonial Sub-Saharan Africa.
Education was prioritized under the Ravalomanana administration from 2002 to 2009, and is compulsory and currently free from ages 6 to 13. The primary schooling cycle is 5 years, followed by 4 years at the lower secondary level and 3 years at the upper secondary level. Primary school fees were eliminated and kits containing basic school supplies were distributed to primary students in this country. Public expenditure on education was 14 % of total government expenditure and 4% of G.D.P in 2008. Primary crowded are classrooms, with average pupil to teacher ratios of 45:1 in 2008.
Demographics
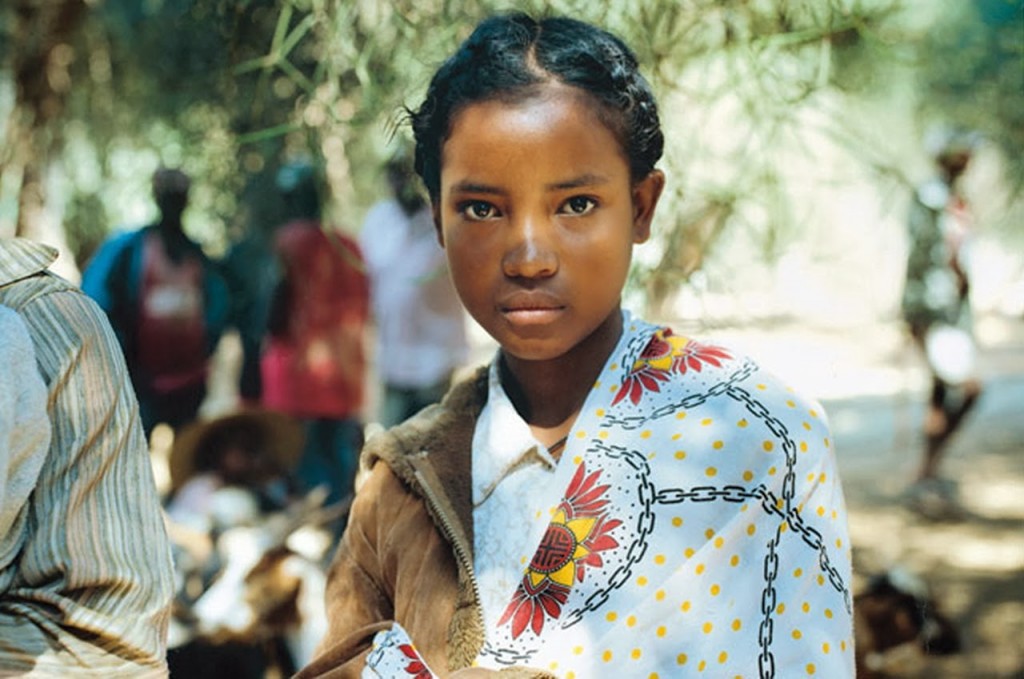

Ethnic diversity
In 2012, the population of Madagascar was estimated at 22 million.
Recent DNA research revealed that the genetic makeup of the average Malagasy person constitutes an approximately equal blend of East African and Southeast Asian genes. The genetics of some communities show a predominance of East African or Southeast Asian origins or some Indian, Arab or European ancestry. The largest coastal ethnic groups are the Betsimisaraka with 15 % and the Sakalava and Tsimihety with 6% each. Comorian, Chinese and Indian minorities are present in Madagascar, as well as a small European populace. The annual population growth rate in Madagascar was approximately 3 % in 2009. The population grew from 2.3 million in 1901 to an estimated 22 million in 2013. In madgascar approximately 43.5 % of the population is younger than 15 years of age, while 55% are between the ages of 15-65.
Religion
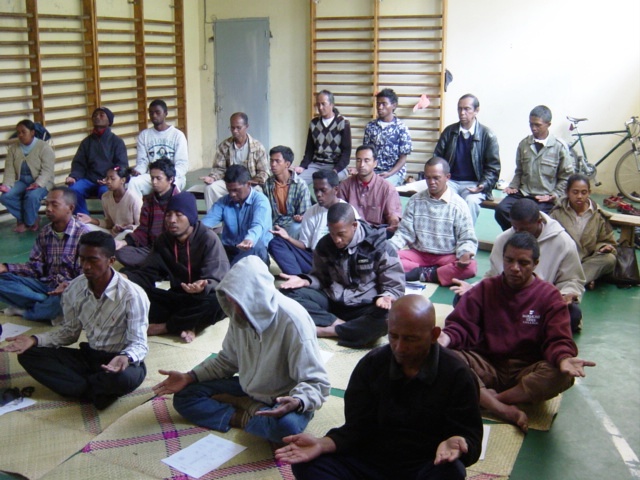

The famadihana is an organization to celebrate the beloved ancestor’s moments, reunite with community and family, and enjoy a festive atmosphere. Residents of neighborhood villages are often invited to attend the party, where rum and food are typically served and a hiragasy troupe or other musical entertainment is always present. Most of people in Madagascar are Christian. In 1818 the LMS sent the first Christian missionaries to the Republic of Madagascar, where they built churches and translated the Bible into the Malagasy language which was a wonderful gift for people here, and then they began to gain converts.
Islam is also practiced on the Republic of Madagascar. Islam was first brought to the Madagascar in the Middle Ages by Somali Muslim and Arab traders, who established several Islamic schools around the island. Today in Madagascar, Muslims constitute 7 % of the population and are largely concentrated in the northwestern provinces of Antsiranana and Mahajanga. Most Hindus in Republic of Madagascar speak Hindi or Gujarati at home.The vast majority of Sunni are Muslims. Muslims are divided between those of Malagasy, Pakistanis, Comorians and Indians. Hinduism was introduced to Madagascar more recently through Gujarati people emigrating from the Saurashtra which is region of India in the late 20th century.
Arts

A wide variety of written literature and oral has developed in the Republic of Madagascar. One of the Madagascar’s foremost artistic traditions is its oratory, which is expressed in the forms of hainteny – poetry, kabary- public discourse and ohabolana-proverbs.
The Ibonia is an epic poem exemplifying these traditions which has been handed down over the centuries in different forms across the Madagascar, and offers insight into the beliefs of traditional and diverse mythologies Malagasy communities.
This tradition was continued by such artists as Joseph Rabearivelo-Jean, who is considered Madagascar’s first modern poet, and one other famous artist is Elie Rajaonarison which is an exemplar of the new wave of African poetry.This island has also developed a rich musical culture, embodied in dozens of regional musical genres such as salegy or hiragasy highland that enliven village gatherings, national airwaves and local dance floors. The plastic arts are also part of the island. In addition to the tradition of lamba production weaving and silk, the weaving of reaffia and other local different plant materials has been used to create a different array of practical items such as baskets, purses floor mats, and hats.
Wood carving has developed art form in Madagascar, with distinct regional styles evident in the architectural elements and decoration of balcony railings. Sculptors create a different of household goods and furniture, wooden sculptures and aloalo funerary posts many of which are created for the tourist market.
Madagascar Food and Drink

Specialities:
- Romazava is a type of beef stew.
- Ravitoto is usually served with shredded cassava leaves.
- Varanga (fried slivers of beef).
- Sesika Vorivorin-kena is beef specialties with vegetables.
- Smalona (stuffed eels).
- Lasary is a colorful chutney usually made from mango, lemon, orange or papaya – or sometimes peanuts, tomato or different vegetables.
- Khimo (beef popular food in Majunga).
- Kabaro (Lima beans with coconut or curry, this kind of food is specialty in Morondava).
The cuisine of Madagascar Island can appear quite dull. Traditionally people in Madagascar eat a large mound of rice with special ingredients, which is served with meat, sauce and different vegetables.
Zebu (kind of beef) steaks are usually excellent and most commonly served with a delicious green peppercorn sauce and different vegetables. Most towns in republic of Madagascar have cheap Chinese eateries, which are usually reliable with independent travelers and very popular. Pizza is popular everywhere in this country. Note that usually hotels in Madagascar tend to offer a set menu or a very limited choice to their customers. Even restaurants with special apparently extensive menu may have a rather restricted number of specialties available outside peak tourist season. Tourist season starts in April and finish in September.
Vegetarian’s people can usually be accommodated easily in this place, even if there are no vegetarian specialties explicitly listed on the menu.
Things to know: The many varieties of food here may be vegetarian or maybe include animal proteins, and different typically feature a sauce flavored with different ingredients such as onion, ginger, garlic, salt, tomato, curry powder, vanilla, less commonly or other herbs or spices. In parts of the arid south and west of Madagascar, pastoral families may replace rice with cassava, maize or sometimes with curds made from fermented zebu milk. A wide variety of savory and sweet fritters as well as other street foods are available across the Madagascar Island, as are diverse temperate-climate and tropical fruits. Locally produced beverages include coffee, herbal teas, teas and fruit juices. Alcoholic drinks are famous in this place too for example rum, wine and beer.

Regional drinks:
- Ranovola – is drink with rice water, made by boiling water in the pan in which rice has just been cooked before. This kind of drink is an acquired taste that divides opinion among travelers in Madagascar.
- Malagasy wine (produced by seven vineyards, and is typically of an average table wine quality; it is produced in red, white, rosé and grey types).
- Litchel – is an aperitif made from pain apple and lychees.
- Rhum arrange – is homemade flavored rums that are available in great variety – produced with various fruit or incidents. This drink is served in large glasses with a lot of ice and lemon.







As far as I know, the first language is Malagasy, the second is French. Actually, most of the Malagasy do not speak French.
May I cite your article in a children’s book that takes place in Madagascar?
thic stincc ahhhhh
This seemed to be a very interesting and introductory look at the country of Madagascar and its relation on the world map. I appreciate the research and diligent work that went into the creation of this writing and I only hope that on my future online information searches I find articles that are as well written and studied as this one is.
sounds good might visit
i know
Where is the citation?
Watching Channel 4 TV program today, May 11, 2019, about young people detained in prison without charge for more than 5 years is very disturbing and contravenes all International Human rights. Please, Please can this be highlighted and resolved. Thanks S G